Intro
The success of your part largely revolves around what machining operation you use to make the part. For big production orders of metal parts, plenty of people use die casting. It’s a fast, low-cost way to make solid parts out of metal.
We’ll teach you all about die casting in this guide — what it is, how it works, and when you should consider using die casting for your parts.
What Is Die Casting?
Die casting is a type of manufacturing operation that entails pushing molten metal into a hollow cavity, also called a die, tooling, or mold. The resulting part is a solid piece of metal that’s been cooled, hardened, and removed from the die.
This operation is a few hundred years old, and you can find it used across multiple industries.
How Does Die Casting Work?
The process seems simple enough, but it’s a lot more complicated in practice. It entails using a hollowed die, molten metal, and pressure to fill the die.
The mold itself is typically two pieces of hardened steel that are clamped together with a small hole for putting in the metal.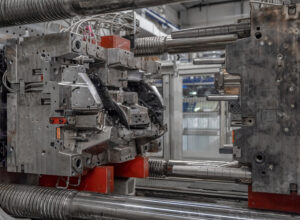
Molten metal is pushed into the die with between 10 and 140 MPa of pressure (which is a lot). The part is then set in place and allowed to cool. When the molten metal cools, it hardens and becomes a solid piece of metal.
The dies will then separate, and the part will be pushed out. After closing back up, the die casting operation is ready to make another part.
To simplify the process, you’ll prep the mold, fill it, eject it, then do minor post-processing steps to the finished part while the die is closed again and the process is repeated.
The Process of Making a Die Casting Mold
The mold is perhaps the most important part of this operation. It’s the only thing responsible for making your final parts. If there are any errors or inconsistencies, then you’ll notice defects on every part that’s created in this process.
To make a die casting mold, our machinists have to use very strong and thermally resistant steel with some sort of heat-treatment. This helps with the durability and wear-resistance of the tooling, allowing you to get more successful parts from a single die.
We typically use CNC machining to make the part from scratch, and it requires some intricate CAD models to go along with the die.
The Two Types of Die Casting
Die casting comes in two different styles: hot chamber and cold chamber. As you might have guessed, the difference has to do with the temperature and how it’s applied. As a customer, you wouldn’t need to choose between the two, it’s up to the machine shop and which option they have in their facility.
All About Hot Chamber Die Casting
A hot chamber die casting machine is more expensive, and it has elements to heat up the metal within the machine. In other words, the die casting machine physically turns the metal into a liquid immediately before pumping it into the cavity.
This allows for faster cycle times but a higher price tag for the machine.
All About Cold Chamber Die Casting
A cold chamber will use a separate furnace to heat up the raw metal before pushing it into the die casting machine. This takes longer and comes with more stress to quickly load metal into the die.
What Materials Can You Use in Die Casting?
Unlike CNC machining, you can’t throw whatever material you want into the die and hope for the best. Since it involves melting down metal into a liquid state, you can only work with metals that have relatively low melting temperatures.
That immediately removes any ferrous metals like stainless steel or cast iron.
Instead, you’ll choose from alloy combinations of aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and tin. In our shop, aluminum alloys are the most common option and they tend to be preferred in a number of industries.
Different Die Casting Applications
You’ll find die-cast parts used in a wide range of different industries and applications. Here are some that we’ve seen in the past:
- Automotive. You can use die casting to create engine brackets, cylinders, and power steering components. Certain paneling and seat frames can be made as well.
- Construction. Often, window frames are made from die casting operations.
- Aerospace. Die-cast parts are used a lot in aerospace since they’re lightweight and each part is consistent.
- Electronics. We’ve made die-cast enclosures, connectors, and housings in the past. With a clever design, you can have a built-in heat sink from the same die casting operation.
Conclusion
We covered a lot about die casting in this intro guide. You learned what it is, how it works, and where you might have seen it in the past. If you want to die cast your next project, reach out to our experts at Rapid Axis. We have run countless die casting jobs over the years, and we’d love to help with yours. Get a free quote today to get started.
