Rapid Axis for Die Casting Services
Rapid Axis provides competitively priced, quality parts; quickly. We provide quicker speed to market within your product design lifecycle with quick turn and high quality Die Cast components. Rapid Axis boasts some of the shortest lead times for Die Cast tooling in the industry. Work with Rapid Axis for the highest level of customer service and quality Die Casting.
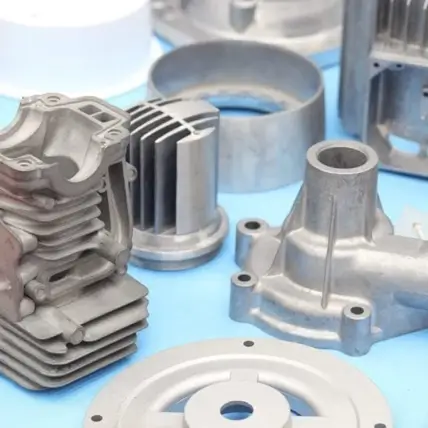
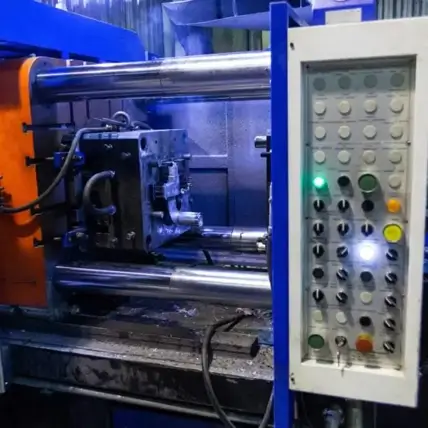
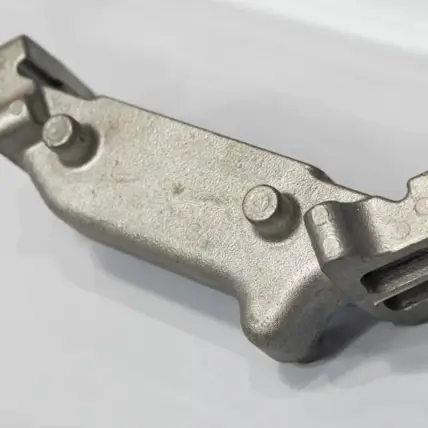



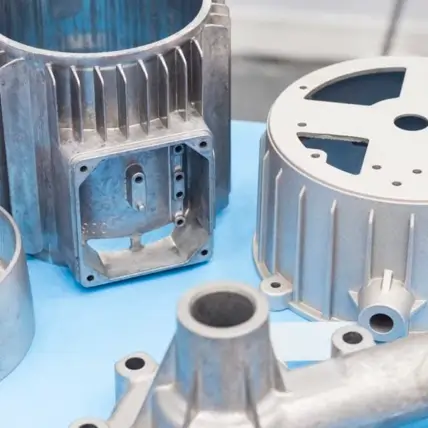
Why Rapid Axis is the best choice for Die Casting Services
Rapid Axis has a superior focus on customer service beyond that of your typical production tooling supplier. We also boast some of the shortest lead time in Die Cast tooling turnarounds in the industry. We provide constant support through your Die Casting project from DFM prior to tooling up, to First Article review and finally all the way through production and finish machining. You can rest assured that your production Die Casting project is in good hands with frequent updates to your project and easy to reach Project Management for any questions or concerns. With both capabilities in pressing, finish machining and surface treatments you’ll receive great components fully finished and ready for your build.
Tools in weeks, not months
Finishing and second op machining supported
Best in industry support
Technical
Tolerances: +/-.005 or better, as tight as +/-.001
Size: Dependent on design, up to 75” squared
Finishing and Secondary Operations: Post-Machining, Inserts, Welding, Brazing, Painting, Polishing, Bead Blasting, Powder Coating, Anodizing, Chem Film, Black Oxide and more….
See Finishes page
Materials: Aluminum, Magnesium, Zinc
See Materials page
What is Die Casting?
Die casting starts with two halves of a hollowed-out mold, called the die. The die can have a series of different cavities in them. Each cavity is the negative image of the part you’re looking to make.
If you’re making metal spheres, then your die will be a square with a spherical ball cut out of the middle.
The die is then filled with molten metal. Since it’s molten, it’s a liquid and will flow and settle in the die. The idea is that the molten metal will fill the entire negative and every corner of the cavity.
The two halves are held together tightly while the molten metal in the die cools down and becomes solid. The halves are then separated, and the metal part is released from the cavity.
The concept behind this casting method is a lot like making a sandcastle. You pack the sand into the bucket, which is the negative of the castle you’re looking to make. In die casting, you fill a negative with molten metal which reflects the final product.
To make the die, a tooling expert will create a design and a machinist will make it either with a DMLS 3D printer or through CNC machining. Tolerances are very important, since any mistake will compound and ruin every part that’s made in the die.
When it comes to material selection, you’ll have to choose from non-ferrous metals. Some of the more common options are aluminum, zinc, nickel, magnesium, and copper. Aluminum die casting in particular produces casts with a high strength-to-weight ratio for more stability.
Die Casting Applications
There are a lot of different applications and benefits for die casting. Our die casting experts came up with this list to help you understand if this option is right for your next project.
Quickly Made Parts
One of the best parts about die casting is that after the Tooling operation you can consistently make parts very quickly. The whole operation can take a few minutes to get a fully-formed, operational piece.
The same piece could take hours or days to make traditionally with a CNC machine.
As a customer, this means that you’ll get parts to your office quicker than ever. This becomes increasingly true as your batch size increases — the hours saved turns into months saved as you order in bulk.
The only caveat is that this process only works if you want the same product made repeatedly. If you want to tweak the design or get a different part, then you’ll have to look at CNC machining or DMLS 3D printing. Tooling can take as little as two weeks for Die Casting or as long as twenty depending on tool material and shots required.
Tolerances are Impressive
The tolerances that a die casting machine has to offer are impressive. At Rapid Axis, our machines can hit tolerances as tight as +/- 0.002 inch per 1st inch then +/- 0.001. With tighter tolerances, you’ll have out-of-spec units less often.
It also allows your assembly to become more reliable. When tolerances start to fluctuate, then suddenly parts don’t fit together and you run into issues on the floor.
To get similar tolerances with CNC machining, you’ll need to pay more for “precision” machining. With a die cast machine, these tolerances are standard and don’t cost you extra.
Reduced Material Scrap
Just like with 3D printing, the die casting process doesn’t rely on cutting away material and wasting it. When you machine a part, you start with a solid block and you cut away features until you’re left with the desired product. With die casting, you’re filling up a mold with molten metal. You’re only using as much metal as the final product needs.
This makes die-cast parts more eco-friendly and it means you’re not wasting money on material that you didn’t even use. There are times when a CNC operation wastes more material than it uses. When you consider order sizes in the hundreds, these extra material costs can add up to a lot.
More Affordable Than CNC Machining
After the initial tooling investment, die casting a part is more affordable than CNC machining the same part. There is an upfront cost associated with making the dies and getting the machine operational, but that cost dilutes as you make more parts.
With CNC machining, the price stays pretty consistent as you order more parts. You might see a slight discount as you order more, but it’s not nearly as affordable as die casting the same part.
The price difference lies in the material cost and manhours required. With a CNC machine, a trained machinist needs to work with the machine every step of the way. A die casting operation is much simpler and more hands-off, with some machines being operator-free for most of it.
The other piece is the material costs. Since die-cast parts only use the amount of metal needed, there’s no scrap. That equates to no wasted material or wasted money.
Get the Same Material Properties as CNC Machining
We keep comparing this manufacturing process to CNC machining, and we should point something out: the material being used is identical between the two methods. When you die-cast a part, the final product will have the same material properties as a CNC machined part of the same material.
You aren’t sacrificing tensile strength in the name of faster, less expensive parts when you choose die cast parts.
